What is Transformer?, Energy Transformer.
- A transformer is a static electrical machine which is used to change the voltage level of the AC power supply.
- It can increase(step up) or decrease(step down) the level of voltage.
- It accomplishes this by electromagnetic induction.
- It does so without any change of the supply frequency.
The term transformer is always related to the power and energy if we think it from the electrical point of view. The transformer can't change the energy or power level of the system. Based on the application sometimes it is called energy transformer again sometimes power transformer.
Working Principle of Transformer
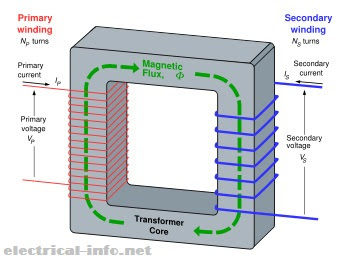
"The transformer works on the basic principle of electromagnetic induction and mutual induction between two coils/windings which are magnetically connected"
- Before going to the theory and laws, we will know the main function what it does.
- There are usually two coils primary coil and secondary coil on the transformer core if we give a power supply across the primary coil at any specific voltage level then the secondary coil will provide the same power with another different voltage level.
- Suppose you have a coil or winding which is supplied by an alternating electrical power source.
- Then the alternating current will passes through the coil and it will create a changing(Amplitude & Direction) or alternating magnetic flux that surrounds the coil.
- Now if another winding is brought close to this winding some portion of this alternating flux will touch or link the second winding.
- Hence there will be an EMF or voltage induced in the second winding as per Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
- If you close the circuit of this second winding the an alternating current will flow through it. This is the basic working principle of a transformer.
What are the main parts of a Transformer?
- Magnetic Core
- Transformer Windings
- Transformer body/tank
- Oil Conservator
- Radiator
- Breather
- Buchholz Relay
Types of Transformer
There are two types based on the construction
1. Core-type transformer.
2. Shell-type transformer.
Core-type transformer
- The windings surround a considerable part of the core.
- The primary and secondary winding are placed on the side limbs.
Shell-type transformer
- The core surrounds a considerable portion of the windings.
- Both the primary and secondary windings are placed on the central limb.
There are two types based on the operation
1. Step-Up transformer.
2. Step-Down transformer.
Step-Up transformer
- It increases the voltage from primary coil to the secondary coil.
- It converts low voltage high current on primary side to high voltage low current on secondary side of a transformer.
Step-Down transformer
- It decreases the voltage from primary coil to the secondary coil.
- It converts high voltage low current on primary side to low voltage high current on secondary side of a transformer.
Some related questions that may raised on your mind.
- What is power transformer?
- What is distribution transformer?
- Why do we use iron core in transformer?
- How deterioration of the transformer oil occurs?
- What are the characteristics of transformer oil?
- Why are iron losses constant at all loads in a transformer?
- What are the basic checklist for a transformer?
- What are the types of transformer oil?
- What is the ideal oil level in transformer oil conservator?
- What would happend if a power transformer designed for operating at 50 Hz were connected to a 500 Hz source of the same voltage?
 |
| Fig: Power Transformer |